Study on Flame Retardancy of Thermoplastic Polyurethane TPU Elastomer
Release time:
2023-11-13 18:15
Source:
Polyurethanes (PUR and PU for short) are polymers composed of urethane-linked organic units. While most polyurethanes are thermoset polymers that do not melt when heated, polyurethanes are also thermoplastic.
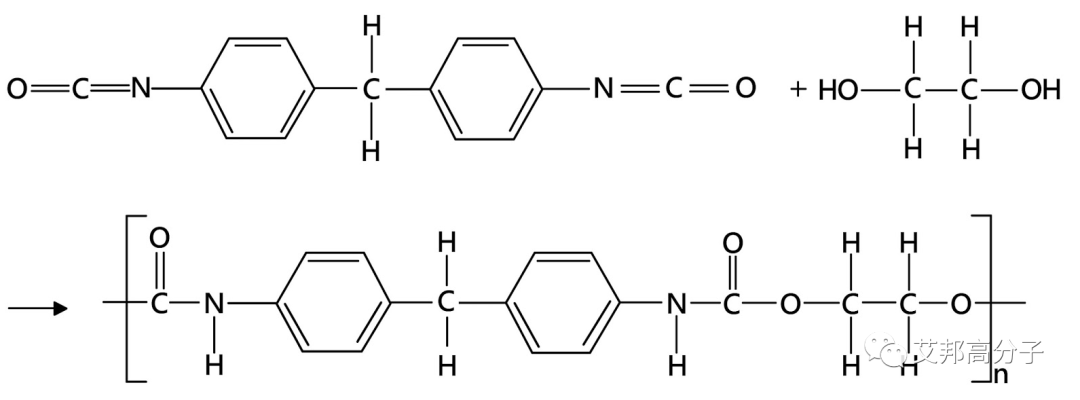
Polyurethane polymerization schematic
Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer (TPU) is a kind of elastic polyurethane which can be heated and plasticized. The molecular structure is a block linear polymer obtained by copolymerization of diisocyanate and polyol. There is no chemical crosslinking, but it has certain physical crosslinking characteristics at the use temperature.

polyurethane elastomer
At present, there are many kinds of TPU developed by people, and the mechanical properties span is also very large, with some excellent properties of rubber and plastic. At the same time, TPU also has excellent wear resistance, aging resistance, high resilience, etc., and is widely used in industry, life, medical, military and other aspects.

Polyurethane foam
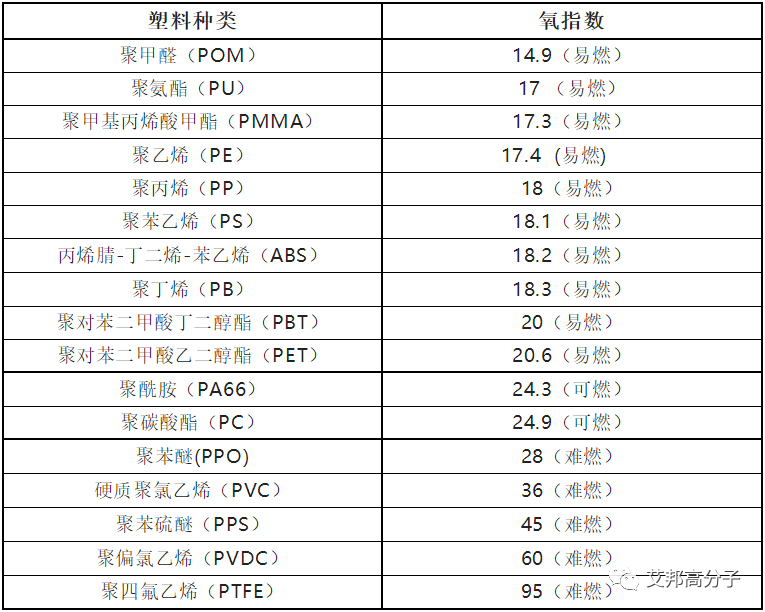
However, TPU also has an obvious disadvantage. Ordinary TPU is flammable and its limiting oxygen index (LOI) is only 16% ~ 18%. In case of fire, it will burn rapidly and decompose to produce a large amount of toxic smoke.
Flame retardant TPU is achieved by incorporating inorganic or organic flame retardant elements, such as some units containing phosphorus, nitrogen, boron, aluminum, magnesium, and halogens, into the TPU substrate. In the early days, halogen flame retardants were widely used in the flame retardant modification of polymer materials, but halogen will produce a lot of toxic gases when burning, so it is slowly eliminated.
At present, people have turned their research focus to more environmentally friendly halogen-free flame retardant technology. The flame retardant modification of TPU can be divided into reactive intrinsic flame retardant modification and additive flame retardant modification according to the combination of flame retardant and polymer substrate. This article will introduce the progress of flame retardant TPU from these two aspects.
reactive flame retardant modification
Reactive flame retardant modification refers to the introduction of flame retardant functional elements or chemical functional groups through chemical bonds in the polyurethane polymer chain structure, so that the TPU polymer chain itself has flame retardant characteristics. At present, the commonly used reactive flame retardants are polyols or isocyanate units containing elements such as phosphorus and nitrogen.
For example, an intrinsically flame retardant TPU is prepared using a phosphorus-containing polyol as a polymerized monomer. Using phosphorus flame retardant polyol to modify TPU, phosphorus element is introduced into the polymer chain through polymerization reaction, which is a part of the polyol structure. In the combustion process, phosphorus element will release in the form of PO · free radical and capture the free radicals generated by the combustion of the polymer matrix, thus quenching the combustion reaction, promoting the carbon formation of the matrix, and achieving the flame retardant effect.
The nitrogen-containing flame retardant is mainly produced by decomposition at high temperature and NH3, N2 and other non-combustible gases play a flame retardant effect. For example, the reactive TPU is prepared by using diisocyanate, dimethylol propionic acid, polyether diol, and a diol (FRC-5) containing phosphorus/nitrogen elements with hydroxyl groups on both sides as monomers, the flame retardancy is significantly improved, and the thermal stability is also improved. Bis-hydroxy liquid phosphate (BBHP) was synthesized using n-butanol, phosphorus oxychloride and 1,4-butanediol as raw materials, and then reacted with 4,4 '-diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI) to produce flame retardant TPU. When the mass fraction of BBHP is 10% ~ 12%, the oxygen index of flame retardant TPU reaches 27%.
Reactive flame retardant modification generally has the advantage of lasting and stable flame retardant effect and less influence on other properties of the material, but the modification process is relatively complex and involves polymerization reaction. At the same time, the requirements for modifiers are also high, only some flame retardant elements or functional groups can be introduced into the TPU molecular chain, so there are not many studies and practical applications. In addition, the flame retardant efficiency of reactive flame retardant technology needs to be further improved.
Addition type flame retardant modification
The advantage of additive flame retardant modification is that the preparation of flame retardant TPU is physical mixing, does not involve chemical reaction, the process is relatively simple, and the flame retardant source is wide, the cost is low, therefore, the research and application of additive flame retardant modification are very extensive.
It should be noted that the added flame retardant needs to consider the compatibility with the matrix, otherwise it is easy to precipitate, which affects the flame retardant effect and the mechanical properties of TPU. Additive flame retardant modification can be divided into inorganic flame retardant addition, organic flame retardant addition, and organic-inorganic composite addition according to the type of flame retardant.
Inorganic flame retardant addition
Inorganic flame retardants are mainly inorganic compounds containing aluminum, boron, silicon, magnesium, titanium and other elements. The flame retardant mechanism of inorganic flame retardants is mainly to reduce the heat generated by the combustion of TPU or to improve the strength and heat insulation effect of the carbon layer to achieve the purpose of flame retardant.
Inorganic flame retardants can be ground into powder or nano-sized, they can be mixed with TPU resin after surface modification, and some complex chemical reactions will occur when the TPU matrix material is burned. Such as the commonly used inorganic flame retardant aluminum hydroxide, when TPU burns, the crystal water in the aluminum hydroxide molecule will be released to form water vapor, reduce the oxygen concentration, and absorb heat at the same time. The alumina particles generated by the dehydration of aluminum hydroxide will also combine with the carbon generated by the combustion of polymer materials to form a solid composite carbon layer, isolating oxygen and making it difficult for the internal polymer to continue to burn.
In recent years, in addition to the traditional inorganic flame retardants, a large number of new inorganic flame retardants have been developed by scientific researchers for TPU flame retardant.
In addition to the effects of strengthening carbon layer and catalyzing carbon formation, some inorganic compounds containing special metal ions also have good smoke suppression effect and have advantages in environmental protection. Therefore, more and more people are paying attention to them. However, the compatibility of inorganic particles with organic polymer TPU is not good, the addition amount is generally low, and a large amount of addition will damage the mechanical properties of TPU.
Organic flame retardant added
Organic flame retardants mainly include early halides and phosphorus and nitrogen organic compounds that are widely concerned by people at present. The flame retardant mechanism of organic flame retardants varies with different components. The high flame retardant efficiency of halides is due to the fact that during combustion, halides can produce free radicals to inhibit the combustion of polymers, and at the same time generate a large amount of non-combustible flue gas and dilute combustible gas to achieve the purpose of flame retardant, but the disadvantage is that the generated flue gas is toxic. Therefore, it is gradually eliminated.
The flame retardant mechanism of phosphide is similar to that of halogen, and it can also generate free radicals to prevent the basic reaction of combustion (oxidation reaction). Its advantage is that it will not produce toxic gases, but also promote carbon formation and improve the strength of carbon layer, so it has attracted much attention.
Nitrogen-containing flame retardants are mainly gas-phase flame retardants. When burning, a large amount of non-combustible gas is generated, which dilutes oxygen and inhibits the oxidation reaction. Some nitrides, such as hindered amines, can also produce free radicals and prevent oxidation reactions.
In recent years, because the flame retardant effect of organic flame retardants containing phosphorus and nitrogen is more obvious, the research on this kind of flame retardant is deep. BDP flame retardant modified TPU was prepared by mixing bisphenol A- bis (diphenyl phosphate)(BDP) with monomer by one-step embedding method. The results show that the oxygen index and UL 94 flame retardant grade of flame retardant TPU increase with the increase of flame retardant BDP content, but its mechanical properties such as tensile strength and 100% elongation modulus increase with the increase of flame retardant content. When the mass fraction of flame retardant BDP is 9%, the comprehensive performance of flame retardant TPU reaches the best, its oxygen index reaches 26%, and the flame retardant grade of UL 94 reaches V-1.
Studies have shown that organic flame retardants have obvious flame retardant effect, good compatibility with TPU substrate, its addition amount can be more than inorganic flame retardants, the impact of mechanical properties is also smaller than inorganic flame retardants, but in the smoke suppression effect is not outstanding, only a small amount of organic flame retardants have a certain smoke suppression effect.
organic-inorganic composite addition
Both inorganic flame retardants and organic flame retardants have their own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, people pay more and more attention to the combination of organic flame retardants and inorganic flame retardants to play a synergistic effect, maximize strengths and avoid weaknesses, and achieve better flame retardant effect.
Aluminum hypophosphite (AHP) and melamine cyanurate (MCA) were compounded and added to TPU to prepare flame retardant TPU material. When adding 11% flame retardant (the mass ratio of AHP to MCA is 1 ∶ 2), the vertical combustion of flame retardant TPU reaches UL 94 V-0 and LOI is 25.2%. The addition of flame retardant AHP/MCA can improve the thermal stability of the composites and promote the char formation of the composites.
Using ammonium polyphosphate (APP), aluminum hypophosphite (AHP) and aluminum diethylphosphinate (ADP) as flame retardants, and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid as synergistic flame retardant and smoke suppressant, a series of TPU composites were prepared by melt blending method, and their flame retardancy and smoke suppression properties were studied. The results show that [EMIM]PF6 as a flame retardant alone has better flame retardant and smoke suppression effect on TPU materials, and as a synergistic flame retardant, it has better flame retardant and smoke suppression effect on TPU composites in synergy with APP, AHP and ADP flame retardants.
After the organic and inorganic flame retardants are combined to form hybrid materials in a certain way, the flame retardant effect is significantly improved compared with the single flame retardant, but the flame retardant modification mechanism involved is also more complex, especially the inorganic-organic synergistic effect, which needs further study.
In general, starting from the monomer structure, the reactive flame retardant modification of introducing flame retardant groups through chemical bonds during polymerization can effectively improve the structural stability and flame retardant durability of the material, but the method is complex and has great limitations. Additive modification, the process is relatively simple, and the source of flame retardants is wide, the performance of composite materials to improve the space, research and application is relatively more.
The added flame retardants have their own advantages and disadvantages. Inorganic flame retardants generally have the advantages of catalytic flame retardant effect, strengthening the carbon layer structure, and smoke suppression, but the disadvantage is that the compatibility with the TPU matrix is not good, the dispersion is poor, the durability is low, and the amount of addition should not be too large. Organic flame retardants are generally easy to mix with the matrix, but also have a catalytic flame retardant effect, but the efficiency is generally not high, and the stability is also lacking. Through the use of organic-inorganic composite, such as organic flame retardant coating inorganic flame retardant, or load organic flame retardant on the two-dimensional inorganic flame retardant, not only can improve the compatibility, but also increase the stability of organic matter, strengthen the flame retardant efficiency. Therefore, the hybrid of organic flame retardants and inorganic flame retardants to play a synergistic effect will be an important development direction of TPU flame retardant modification research in the future.
We use optional cookies, improve your experience on our website through social media connections and other means, and advertise personalized ads based on your online activities. If you refuse the optional cookies, we will only use the cookies necessary to provide you with the service. Privacy Statement

Mobile website

Alibaba
Jiangsu Liside New Material Co., Ltd
Tel: +86-523-88960000
E-mail: liside@liside.com
Add: No. 88 Zhonghua East Road, Tianmushan Street, Jiangyan District, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province
MD: No. 13 Zhengtai Qiling Garden, Luotang Street, Jiangyan District, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province
Copyright: Jiangsu Liside New Material Co., Ltd
SAF Coolest v1.3.1.2 设置面板 HTESX-ZTUS-OESDE-ZFX
无数据提示
Sorry, the current column is being updated, please stay tuned!

